1.knee pain location chart ? 2.what is the knee thing ? 3.knee pain when bending? 4.my knee hurts when I bend it and straighten it 5.knee hurts when bent 6.knee pain when squatting? All these questions will be answered in below topic.
Knee pain is a common health issue that can impact people of all ages, from young children to the elderly. One of the largest and most important joints in the body, responsible for supporting the body’s weight, facilitating movement, and absorbing various stresses during physical activities.
Importance of Knowing About Knee pain:
There are various reasons why it’s critical to understand knee pain.
1. Effect on day-to-day functioning: Walking, climbing stairs, and engaging in sports and leisure activities are just a few of the everyday tasks that can be made considerably more difficult by knee discomfort. Severe knee discomfort may result in loss of freedom as well as disability.
2. Quality of Life: Continuous knee pain can make impact physically, mentally and emotionally. It can results in some other symptoms like sleep disturbances, mood changes, and social withdrawal, contributing to a weakened sense of health and happiness.
3. Complications Risk: Disregarding or ignoring knee pain increases the chance of developing other issues, such as joint damage, decreased mobility, and a higher chance of accidents and falls. To avoid long-term effects and maintain knee function, prompt diagnosis and adequate treatment are crucial.
4.Early Intervention: Finding the source of knee discomfort early on enables prompt intervention and treatment, which may stop the disease’s progression and enhance results. Additionally, prompt and efficient return to regular activities might be facilitated by early diagnosis.
Important Components of the Knee Joint:
1. Bones: The femur (thigh bone), tibia (shinbone), and patella (kneecap) are the three bones that make up the knee joint. These bones are surrounded by muscles and tendons that give the joint support and motion, and ligaments hold them together.
2. Articular Cartilage: Articular cartilage is a smooth, slick tissue that covers the ends of the femur, tibia, and patella. By facilitating smooth bone-to-bone movement and reducing friction, this cartilage shields the joint surfaces from deterioration during motion.
3. Meniscus: The knee joint contains two crescent-shaped cartilage structures called meniscus (singular: meniscus), which act as shock absorbers and help distribute weight evenly throughout the joint.
4. Ligaments: The knee joint is supported by four main types of ligaments:
• The anterior cruciate ligament, or ACL
• The posterior cruciate ligament, or PCL.
• The medial collateral ligament, or MCL
• Lateral Collateral Ligamento (LCL) As the connecting tissue between the bones of the knee joint, these ligaments help to minimize excessive motion and rotational pressures while maintaining stability and integrity.
5.Tendons: A robust, fibrous connective tissue, tendon attaches muscles to bones. Because they transmit the force generated by muscles to the bones, allowing motion and stabilizing joints, they are vital to the musculoskeletal system. Collagen fibers are generally organized in parallel bundles to give tendon strength and suppleness.
Common Causes of Knee Pain:
1.Ligament injuries (ACL, PCL, MCL, LCL).
2.Meniscal tears.
3.Osteoarthritis.(wear and tear of joint cartilage)
4.Rheumatoid arthritis.
5.Patellofemoral pain syndrome (runner’s knee).
6. Bursitis.
7. Tendonitis, including IT band syndrome and patellar tendinitis.
8.Patellar dislocation or subluxation.
Importance of Identifying Knee Pain Location:
Knee pain can manifest in various regions of the knee, including the front (anterior), inner side (medial), outer side (lateral), and back (posterior). Identifying the specific location of knee pain is crucial for several reasons:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Pinpointing the exact location of knee pain provides valuable clues for healthcare providers to accurately diagnose the underlying cause. Depending on where the discomfort is, several knee tissues, including ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and bones, may be impacted.
- Targeted Treatment: Once the cause of knee pain is identified, healthcare providers can develop a targeted treatment plan tailored to address the specific issue. Treatment modalities may include rest, physical therapy, medication, injections, or surgery, depending on the underlying condition.
- Preventive Measures: Understanding the location of knee pain can help individuals take preventive measures to avoid exacerbating the condition. By modifying activities, using supportive devices (e.g., braces or orthotics), or practicing proper body mechanics, individuals can reduce the risk of further injury or worsening symptoms.
Knee Pain Location Chart
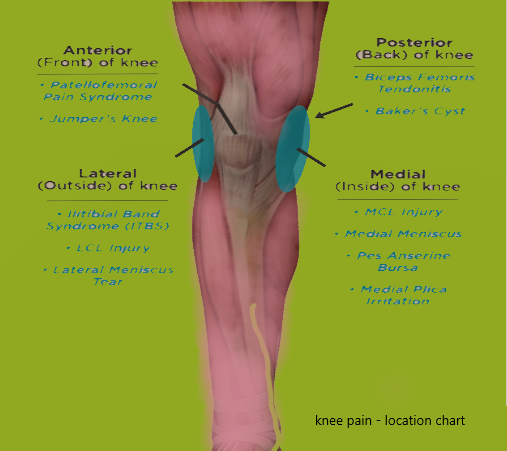
1. Anterior Knee Pain:
- This part of the knee is situated in front, directly beneath the patella (kneecap).
- Common causes of anterior knee pain include patellar tendonitis, patellar tracking disorder, and patellofemoral pain syndrome (runner’s knee).
- Pain, tenderness, swelling, and discomfort during bending over, crouching, or climbing stairs are possible symptoms.
2. Medial Knee Pain:
- Medial knee pain occurs on the inner side of the knee joint.
- Common reasons include injuries to the medial collateral ligament (MCL), medial meniscus tears, and osteoarthritis affecting the inside compartment of the knee.
- Pain, edema, instability, and locking or clicking sensations during movement are possible symptoms.
3. Lateral Knee Pain:
- Lateral knee pain is felt on the outer side of the knee joint.
- Causes may include lateral collateral ligament (LCL) injury, lateral meniscus tear, iliotibial (IT) band syndrome, or osteoarthritis affecting the outer compartment of the knee.
- Pain, tenderness, swelling, and an unstable or giving-way feeling are some symptoms.
4. Posterior Knee Pain:
- Posterior knee pain is located at the back of the knee joint.
- Causes may include hamstring tendonitis, popliteal cyst (Baker’s cyst), or posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) injury.
- Pain, stiffness, edema, and trouble completely extending the knee are possible symptoms.
Symptoms of Knee Pain:
Pain: Knee pain can range from dull aches to sharp, stabbing sensation.
Swelling: Edema or swelling around the knee joint is a common symptoms.
Stiffness: Reduced range of motion and stiffness in the knee are often experienced.
Instability: A feeling of instability or the knee “giving way” may occurs.
Clicking/Popping: Clicking, popping, or cracking sounds within the knee joint can be present.
Diagnosing Knee Pain:
1.Medical History: Gathering information about the onset, duration, and severity of the pain, as well as any relevant medical history.
2.Physical Examination: Assessing the knee joint for signs of swelling, tenderness, instability, and range of motion.
3.Imaging Tests: Utilizing X-rays, MRI, or CT scans to visualize the internal structures of the knee and identify any abnormalities.
4.Laboratory Tests: Conducting blood tests or joint fluid analysis to check for inflammation, infection, or underlying medical conditions.
5.Specialized Tests: Performing specific tests to evaluate ligament stability, meniscal integrity, or other suspected issues.
6.Clinical Assessment: Formulating a differential diagnosis based on the findings from the history, physical exam, and diagnostic tests.
Treatment Options for Knee Pain
Knee pain can be debilitating and significantly impact daily activities. Reducing pain, improving function, and addressing the underlying cause are the objectives of available treatment approaches.. Here are some common treatment modalities:
- 1. Conservative Treatments:
- Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation (RICE): Resting the knee, applying ice packs, compressing the knee with a bandage, and elevating it can help reduce pain and swelling.
- Pain management: For mild to moderate pain, over-the-counter medications such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medicines (NSAIDs) can be used.
- Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can design a personalized exercise program to strengthen muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and promote joint stability.
- Bracing or Orthotics: Knee braces or orthotic devices can provide support, stability, and alignment, reducing strain on the knee joint.
2. Medications:
- Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids directly into the knee joint can help reduce inflammation and provide temporary pain relief.
- Viscosupplementation: Injections of hyaluronic acid (a lubricating fluid) into the knee joint can improve joint lubrication and reduce pain in some cases of osteoarthritis.
3. Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Lubrication Injections: Injecting lubricating substances (e.g., hyaluronic acid) into the knee joint can reduce friction and improve mobility.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP injections use concentrated platelets from the patient’s blood to promote tissue healing and reduce inflammation.
- Radiofrequency Ablation: This technique produces long-lasting pain relief by using heat to damage the nerve fibers that send pain signals from the knee joint.
4.Surgical Interventions:
- Arthroscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery performed using a tiny camera and specialized instruments to diagnose and treat various knee conditions, such as meniscal tears or ligament injuries.
- Partial or Total Knee Replacement: In severe cases of arthritis or joint damage, partial or total knee replacement surgery may be recommended to replace damaged joint surfaces with artificial implants.
Preventing Knee Pain:
Adopting healthy lifestyle practices, preserving appropriate knee mechanics, and abstaining from risky activities are all important steps in preventing knee pain. Here are some strategies for preventing knee pain:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess body weight puts additional stress on the knee joints, increasing the risk of developing knee pain and arthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight through balanced nutrition and regular exercise can reduce strain on the knees.
- Regular Exercise: Exercises that strengthen the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calves—muscles that surround the knee—can support the knee joint and lower the risk of injury. Low-impact exercises like swimming, cycling, or brisk walking can improve knee strength and flexibility without putting excessive strain on the joints.
- Proper Warm-up and Cool-down: Before engaging in physical activity, it’s essential to warm up the muscles with dynamic stretching and light aerobic exercises to increase blood flow and flexibility. Cooling down with static stretches after activity can help prevent muscle tightness and reduce the risk of injury.
- Use Proper Footwear: Wearing supportive footwear with cushioning and shock absorption can help reduce impact on the knees during physical activities. Avoiding high heels or shoes with inadequate support can also help maintain proper knee alignment.
- Practice Good Posture and Body Mechanics: Maintaining good posture and using proper body mechanics during daily activities can help reduce stress on the knees. Avoid activities that involve repetitive or excessive bending, kneeling, or squatting, as these movements can strain the knee joint.
- Avoid Overuse and High-Impact Activities: Limiting participation in high-impact sports or activities that place repetitive stress on the knees, such as running or jumping, can help prevent overuse injuries and protect joint health. Cross-training with low-impact exercises and incorporating rest days into your workout routine can give the knees time to recover and prevent overuse injuries.
- Listen to Your Body: Pay attention to any warning signs of knee pain or discomfort during physical activity. To stop more damage, you should relax and be checked out by a medical professional if you have discomfort, swelling, or instability in your knee joint.



